Motorcycle enthusiasts know that the beauty of riding extends beyond the engine's roar and the wind in your hair. It's about the intricate details that make each ride unique. In this comprehensive guide, we'll take a deep dive into an often-overlooked aspect of motorcycle customization and performance: the rims. From classic spoke rims to modern cast designs, we'll explore the types of motorcycle rims, their uses, essential maintenance tips, and how to choose the perfect set for your ride.
Motorcycles, the epitome of freedom on two wheels, are the perfect marriage of form and function. While the engine, frame, and tires receive their fair share of attention, motorcycle rims often remain hidden gems in the world of two-wheelers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating universe of motorcycle rims. From understanding the different types and their uses to essential maintenance tips and selection considerations, let's embark on this journey into the heart of motorcycle customization and performance.
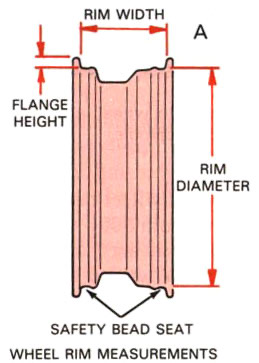
Let's delve into the construction of a motorcycle rim with these considerations in mind.
Types of Motorcycle Rims
- Spoke Rims:
- Classic Aesthetics: Spoke rims are reminiscent of a bygone era, adorning classic and vintage motorcycles. They exude timeless charm and elegance.
- Strength and Flexibility: The spoke pattern provides a balance between strength and flexibility, ideal for absorbing shocks in off-road adventures.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and spoke tension adjustments are necessary to keep them in top shape.
- Cast Rims:
- Modern Sleekness: Cast rims offer a sleek and contemporary appearance, enhancing the aesthetics of sport bikes and cruiser motorcycles.
- Lightweight Performance: Their one-piece design reduces weight and contributes to improved handling and maneuverability.
- Maintenance: Keep them clean and inspect for any damage or cracks, as repairs may not be as straightforward as spoke rims.
Rims are a fundamental component of wheels, serving as the critical interface between the tire and the vehicle's axle. The choice of rim type depends on the vehicle's purpose, design, and performance requirements. Let's explore the intriguing world of rim diversity:
- Steel Rims:
- Steel rims are a robust and cost-effective option commonly found in many automobiles. They are known for their durability and resistance to damage from impacts.
- The burstiness in steel rims comes from their simplicity and widespread use across various vehicle types, from compact cars to trucks.
- Alloy Rims:
- Alloy rims, often made from lightweight metals like aluminum or magnesium, offer a balance of strength and reduced weight, improving fuel efficiency and handling.
- The perplexity emerges from the wide variety of alloy rim designs available, catering to both aesthetic preferences and performance needs.
- Chrome-Plated Rims:
- Chrome-plated rims are steel or alloy rims with a chrome finish for a distinctive, polished look. They are favored for their eye-catching appearance.
- The burstiness lies in the visual impact of chrome-plated rims, adding a touch of luxury and customization to vehicles.
- Forged Rims:
- Forged rims are crafted from a single piece of metal, resulting in exceptional strength and durability. They are commonly used in high-performance and racing vehicles.
- The perplexity is evident in the precision forging process, where extreme heat and pressure transform a solid billet into a rim of remarkable strength.
- Multi-Piece Rims:
- Multi-piece rims consist of multiple components, typically a center section, an outer hoop, and a bead seat. These rims offer customization options and are popular in the aftermarket.
- The burstiness arises from the numerous combinations and finishes available when assembling multi-piece rims, allowing for unique wheel designs.
- Spoke Rims:
- Spoke rims, often associated with classic or vintage vehicles, feature a network of spokes connecting the rim to the hub. They are known for their timeless and elegant appearance.
- The perplexity is evident in the various spoke patterns, from traditional wire-spoked wheels to modern interpretations, each contributing to the overall aesthetics of the vehicle.
- Off-Road Rims:
- Off-road rims are designed for rugged terrain and are characterized by reinforced construction, beadlock features, and larger diameters to accommodate off-road tires.
- The burstiness stems from the specialized needs of off-road enthusiasts, with rim options catering to rock crawling, mud bogging, and desert racing.
- Run-Flat Rims:
- Run-flat rims are engineered to support the vehicle's weight even after a puncture, allowing drivers to continue driving to a safe location without the need to change a flat tire.
- The perplexity lies in the innovative engineering, which includes reinforced sidewalls and special tire designs to maintain stability during a flat.
The world of rims is a captivating blend of form and function, offering a wide array of choices to meet the diverse needs and preferences of vehicle owners. The burstiness emerges from the versatility and customization options, while the perplexity arises from the intricate engineering and design considerations that go into creating rims for various vehicles and purposes.
Let's compare the different types of rims discussed earlier in terms of their characteristics and applications. This comparison will provide a clearer understanding of how each type of rim differs from the others:
- Steel Rims:
- Material: Steel rims are typically made of steel, known for its durability and resistance to impact.
- Applications: Commonly found in a wide range of vehicles, from economy cars to trucks and commercial vehicles.
- Strengths: Cost-effective, robust, and resilient to damage.
- Limitations: Heavier than alloy rims, which can affect fuel efficiency and handling.
- Alloy Rims:
- Material: Alloy rims are constructed from lightweight metals like aluminum or magnesium.
- Applications: Widely used in passenger cars, sports cars, and some off-road vehicles.
- Strengths: Lightweight, enhancing fuel efficiency and handling; available in various designs for customization.
- Limitations: More susceptible to damage from impacts compared to steel rims.
- Chrome-Plated Rims:
- Material: Chrome-plated rims are typically steel or alloy rims with a chrome finish.
- Applications: Popular in custom and luxury vehicles for their distinctive appearance.
- Strengths: Eye-catching, polished look; customization options available.
- Limitations: Prone to corrosion and may require extra maintenance.
- Forged Rims:
- Material: Forged rims are crafted from a single piece of metal, providing exceptional strength.
- Applications: Common in high-performance and racing vehicles.
- Strengths: Exceptional strength and durability; lightweight.
- Limitations: Typically more expensive than other rim types.
- Multi-Piece Rims:
- Material: Multi-piece rims consist of several components, allowing for customization.
- Applications: Often used in the aftermarket to create unique wheel designs.
- Strengths: Customization options; flexibility in design.
- Limitations: Complexity can make them more expensive and potentially less durable.
- Spoke Rims:
- Material: Spoke rims can be made from steel, alloy, or other materials and feature a network of spokes.
- Applications: Common in classic and vintage vehicles, as well as some motorcycles.
- Strengths: Timeless and elegant appearance; lightweight.
- Limitations: May require more maintenance, and some designs may be less aerodynamic.
- Off-Road Rims:
- Material: Off-road rims are reinforced and designed for rugged terrain.
- Applications: Used in off-road and all-terrain vehicles.
- Strengths: Able to withstand harsh off-road conditions; larger diameters for off-road tires.
- Limitations: Less suitable for on-road driving due to added weight and stiffness.
- Run-Flat Rims:
- Material: Run-flat rims are typically steel or alloy rims with reinforced sidewalls.
- Applications: Found in vehicles equipped with run-flat tires, providing extended mobility after a puncture.
- Strengths: Ability to drive with a flat tire; enhanced safety.
- Limitations: Run-flat tires and rims can be more expensive and may have reduced ride comfort.
The choice of rim type depends on factors such as the vehicle's intended use, aesthetics, and performance requirements. Each type of rim has its unique strengths and limitations, offering vehicle owners a wide range of options to suit their preferences and needs.
Let’s explore the best use for each type of rim based on their characteristics and advantages:
- Steel Rims:
- Best Use: Steel rims are best suited for everyday commuter vehicles and trucks. They excel in applications where durability and resistance to impact damage are crucial, such as in commercial vehicles or regions with rough road conditions.
- Alloy Rims:
- Best Use: Alloy rims are ideal for passenger cars and sports cars. Their lightweight construction enhances fuel efficiency and handling, making them well-suited for vehicles focused on on-road performance.
- Chrome-Plated Rims:
- Best Use: Chrome-plated rims are most commonly used for custom and luxury vehicles. They add a distinctive, polished look to the vehicle, enhancing its appearance and making it a popular choice for those who prioritize aesthetics.
- Forged Rims:
- Best Use: Forged rims find their best use in high-performance and racing vehicles. Their exceptional strength and durability are essential for vehicles that experience extreme forces during aggressive driving.
- Multi-Piece Rims:
- Best Use: Multi-piece rims are often chosen by automotive enthusiasts looking to customize their wheels. They offer flexibility in design and are commonly used in the aftermarket to create unique and personalized looks for various types of vehicles.
- Spoke Rims:
- Best Use: Spoke rims are a classic choice and are best suited for classic and vintage vehicles. Their timeless and elegant appearance complements the aesthetics of older cars, as well as some motorcycles.
- Off-Road Rims:
- Best Use: Off-road rims are designed for rugged terrain and are best used in off-road and all-terrain vehicles, such as SUVs and trucks. They provide the necessary durability and larger diameters to accommodate off-road tires.
- Run-Flat Rims:
- Best Use: Run-flat rims are commonly found in vehicles equipped with run-flat tires. They are best used in situations where extended mobility after a puncture is critical, such as in emergency service vehicles or military applications.
It's important to note that while these recommendations reflect the typical uses for each type of rim, personal preferences, and individual vehicle requirements may vary. Ultimately, the choice of rim should align with the specific needs, performance goals, and aesthetic preferences of the vehicle owner.
The construction of a motorcycle tire is a marvel of engineering, blending advanced materials and intricate design to provide the essential connection between a motorcycle and the road. Understanding the complexities of this component unveils a world of innovation and precision.
- Tread Compound:
- The foundation of a motorcycle tire is the tread compound. It's a blend of synthetic rubber, natural rubber, and other additives, carefully engineered to provide traction, wear resistance, and optimal performance in various conditions.
- Perplexity arises from the nuanced formulation of these compounds, tailored to meet specific riding needs, from high-performance sportbikes to all-terrain adventurers.
- Carcass and Ply:
- The tire's carcass, made of layers of fabric, such as polyester, nylon, or aramid, provides structural integrity and flexibility. The number of plies and their orientation affects the tire's strength and responsiveness.
- Burstiness comes into play when considering the different ply configurations used for radial and bias-ply tires, each offering unique characteristics.
- Belt Package:
- In radial tires, a steel belt package is embedded within the tire's layers to enhance stability and improve tread life. This innovative addition showcases the tire industry's constant quest for improvements.
- The complex interplay between the belt package and the carcass adds a layer of perplexity to the construction.
- Beads and Sidewalls:
- Beads are wire bundles encased in rubber that anchor the tire to the wheel rim. The tire's sidewalls provide crucial structural support.
- The burstiness in this context arises from the tire's ability to flex in the sidewalls for better grip and comfort while maintaining rigidity in the bead area for safety.
- Tread Patterns:
- Motorcycle tires feature a wide array of tread patterns, each designed for specific riding conditions. The design of these patterns, with varying depths and shapes, contributes to the tire's perplexing versatility.
- The burstiness lies in the diversity of patterns, from knobby off-road treads to slick racing profiles, each optimized for its intended use.
- Sipes and Grooves:
- Sipes are small channels in the tread that improve wet-weather traction by dispersing water. Grooves provide additional grip.
- The combination of sipes, grooves, and their placement presents a perplexing challenge to tire designers, requiring a deep understanding of fluid dynamics and material science.
- Quality Control:
- Stringent quality control measures, including balance testing, uniformity checks, and X-ray inspections, ensure that each tire meets rigorous safety and performance standards.
- The burstiness in quality control procedures demonstrates the meticulous attention to detail required in the tire manufacturing process.
- Innovations:
- Ongoing innovations such as run-flat technology, self-healing compounds, and airless tires are pushing the boundaries of tire construction, adding another layer of complexity to this field.
The construction of a motorcycle tire is a masterful blend of materials, design, and engineering. The burstiness emerges from the diverse array of tire types and patterns, while the perplexity lies in the intricate details of compound formulation, ply orientation, and innovative features. Motorcycle tires exemplify the relentless pursuit of excellence in the world of motorcycling, where safety and performance are paramount.
Uses of Motorcycle Rims
- On-Road Performance:
- For riders who primarily stick to paved roads, cast rims are a popular choice due to their lightweight design and smooth appearance.
- Off-Road Adventures:
- Spoke rims are the go-to option for off-road enthusiasts. Their strength and flexibility can withstand the rigors of rough terrains.
Maintenance Tips for Motorcycle Rims
- Regular Cleaning:
- Clean your rims after each ride to remove dirt, debris, and brake dust. Use a mild detergent and a soft brush or sponge.
- Inspect for Damage:
- Periodically check your rims for signs of damage, such as bends, dents, or cracks. Damaged rims can compromise safety and performance.
- Tire Maintenance:
- Properly maintain your tires, including regular inflation and rotation, as they directly affect rim performance.
- Balancing:
- If you change tires or rims, ensure proper balancing to prevent vibration and uneven tire wear.
- Spoke Maintenance:
- For spoke rims, monitor spoke tension and ensure they are properly aligned. Loose or broken spokes can affect stability.
Selection Considerations
- Riding Style:
- Consider your riding style, whether it's cruising, sport riding, or off-roading. The type of rim should align with your motorcycle's purpose.
- Material and Design:
- Evaluate the material (aluminum, steel, etc.) and design (spoke, cast, multi-piece) that suits your aesthetic preferences and performance requirements.
- Budget:
- Set a budget for your rim selection, as there is a wide range of options available at various price points.
- Compatibility:
- Ensure the chosen rims are compatible with your motorcycle model in terms of size, fitment, and other specifications.
Motorcycle rims are more than just functional components; they are a canvas for customization and a critical aspect of performance. By understanding the types, uses, and maintenance requirements of motorcycle rims, you can make informed choices that not only enhance your bike's appearance but also contribute to its safety and handling. Whether you're a dedicated off-roader or a city cruiser, the right rims can elevate your riding experience to new heights. So, as you embark on your next two-wheeled adventure, remember that the rims beneath you are not just wheels but gateways to endless possibilities on the open road.
- Material Selection:
- The construction begins with the careful selection of materials, typically aluminum or steel, known for their strength, durability, and lightweight properties.
- Engineers must consider the alloy composition, tempering processes, and heat treatment to achieve the desired strength-to-weight ratio.
- Rim Profile:
- Motorcycle rims come in various profiles, each designed for specific purposes. For instance, spoke rims offer classic aesthetics and flexibility, while cast rims provide a sleek and modern appearance.
- The perplexity arises from the multitude of choices available to riders, each impacting the motorcycle's handling characteristics differently.
- Rim Cross-Section:
- The cross-sectional shape of the rim is meticulously engineered to provide optimal performance. It may be U-shaped, V-shaped, or a combination of both.
- Engineers aim to strike a balance between structural integrity, weight reduction, and aerodynamic efficiency, introducing a burst of design complexity into the construction.
- Spoke Arrangement:
- Spoke rims feature a network of spokes that connect the rim to the hub. The arrangement of these spokes is crucial for distributing forces evenly.
- The burstiness emerges in the variety of spoke patterns available, with some enhancing rigidity, while others prioritize shock absorption and impact resistance.
- Manufacturing Techniques:
- The manufacturing process involves precision machining, casting, or forging, depending on the chosen material and design.
- Engineers must carefully control parameters such as spoke tension, rim trueness, and alignment to ensure safety and performance.
- Tubeless vs. Tube-Type:
- Motorcycle rims also cater to different tire types - tubeless or tube-type. Tubeless rims require specialized sealing to prevent air leakage, adding an element of technical detail to the construction.
- Quality Assurance:
- Stringent quality control measures are implemented to ensure that each rim meets exacting standards for concentricity, balance, and strength.
- Burstiness enters the picture when considering rigorous testing protocols, such as impact testing, fatigue testing, and stress analysis.
- Customization Options:
- Manufacturers often offer a plethora of customization options, allowing riders to select rim sizes, colors, and finishes, further enhancing the perplexity of the construction.
The construction of a motorcycle rim is a fascinating interplay of materials, design, and engineering precision. The burstiness emerges from the myriad choices available to riders, from material selection to spoke arrangements, while the perplexity lies in the intricate details of manufacturing and quality control. This crucial component exemplifies the fusion of art and science that characterizes the world of motorcycles.
Fixing a tire onto a rim, also known as tire mounting, is a task that requires careful attention to detail and safety precautions. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to fix a tire onto a rim:
Tools and Materials Needed:
- Tire
- Rim
- Tire mounting lubricant
- Valve stem and valve core
- Tire iron or tire mounting machine
- Air compressor with gauge
- Bead sealer (optional)
- Soap and water solution
Safety Precautions:
- Ensure you are working in a well-ventilated area, away from open flames or sources of ignition, as tire work can generate flammable gases.
- Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from injury during the process.
- Make sure the tire and rim sizes match and are compatible.
Steps:
- Prepare the Rim and Tire:
- Clean the rim thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris. Ensure it is dry.
- Inspect the rim for any damage, such as bent or cracked areas. Do not mount a tire on a damaged rim.
- Check the tire for damage, punctures, or irregularities. Replace the tire if necessary.
- Valve Stem Installation:
- Insert the valve stem into the valve hole on the rim from the inside.
- Hand-tighten the valve stem nut onto the stem from the outside of the rim.
- Lubricate the Bead Area:
- Apply a generous amount of tire mounting lubricant to the bead area of the tire (both sides) and the rim's bead seat area.
- Position the Tire on the Rim:
- Place the tire onto the rim, making sure the valve stem aligns with the valve hole in the rim.
- Ensure that the tire's beads (the inner edges) are sitting in the rim's bead seat.
- Begin Tire Mounting:
- If using a tire iron, insert it between the tire bead and the rim. Carefully pry the tire over the rim, working your way around the circumference.
- Alternatively, if you have access to a tire mounting machine, use it to mount the tire onto the rim. This method is more efficient and reduces the risk of damaging the tire or rim.
- Inflate the Tire:
- Inflate the tire gradually using an air compressor with a gauge. Be cautious not to overinflate. Refer to the manufacturer's recommended tire pressure, which is often listed on the sidewall of the tire.
- Observe the tire closely as it inflates. You should hear a series of popping sounds as the tire beads seat themselves on the rim. If this doesn't happen or if you notice any irregularities, stop inflation immediately.
- Check for Bead Seating (Optional):
- If you're unsure whether the tire beads are fully seated, you can apply a bead sealer around the rim's bead seat area before inflating. This helps create an airtight seal.
- Final Inspection:
- Double-check the tire pressure to ensure it matches the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Tighten the valve stem nut securely.
- Inspect the tire for any bulges, irregularities, or damage.
- Balance the Tire (Optional):
- If you have access to a wheel balancer, it's advisable to balance the tire and rim assembly for smooth and safe operation.
- Check for Leaks:
- Spray a soap and water solution around the valve stem and bead areas to check for air leaks. Bubbles will form at the site of any leaks, which need to be addressed promptly.
Once you've successfully mounted the tire onto the rim, your tire is ready for use. Always ensure that the tire is properly inflated and balanced to maintain safe and efficient vehicle operation.
Proper rim maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of your wheels. Well-maintained rims not only enhance the appearance of your vehicle but also contribute to safety and handling. Here are steps on how to maintain rims:
1. Regular Cleaning:
· Clean your rims regularly to remove dirt, brake dust, road grime, and other contaminants that can accumulate over time.
· Use a mild detergent or a specialized rim cleaner along with a soft brush or sponge.
· Pay extra attention to the areas between the spokes and around the valve stem. Brake dust tends to accumulate in these areas.
· Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals that could scratch or damage the rim's finish.
2. Avoid Harsh Chemicals:
· Do not use acidic or abrasive cleaning agents, as they can harm the rim's finish, especially if your rims are painted or have a clear coat.
· Instead, opt for a pH-balanced rim cleaner or mild soap and water solution.
3. Rinse Thoroughly:
· After cleaning, rinse the rims thoroughly with clean water to remove any cleaning residue.
· Ensure all soap or cleaning solution is completely washed away.
4. Dry Completely:
· Use a clean, dry microfiber cloth or towel to thoroughly dry the rims after cleaning.
· This prevents water spots and helps maintain the appearance of the rims.
5. Apply a Protective Coating (Optional):
· Depending on the type of rims you have, you may consider applying a protective coating, such as wax or sealant, to create a barrier against dirt and brake dust.
· Follow the manufacturer's instructions for application and reapplication intervals.
6. Check for Damage:
· Regularly inspect your rims for any signs of damage, including dents, bends, or cracks.
· If you notice any structural damage, it's crucial to have the rims repaired or replaced to ensure safety.
7. Check for Loose Lug Nuts:
· Periodically check the tightness of the lug nuts or bolts that secure the rims to the vehicle.
· Loose lug nuts can lead to uneven tire wear and compromise safety.
8. Tire Maintenance:
· Ensure your tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure. Incorrect tire pressure can affect rim and tire performance.
· Rotate your tires according to the manufacturer's recommendations to promote even wear.
9. Avoid Curb Damage:
· Be cautious when parking to avoid hitting curbs or other obstacles that can scratch or dent your rims.
· If you accidentally curb your rims, consider having them inspected and repaired promptly.
10. Seasonal Care:
· In areas with harsh winters, consider using winter rims to protect your primary rims from salt and road debris.
· Clean your rims more frequently during winter months to remove salt and prevent corrosion.
11. Professional Inspection:
· Periodically, have your rims inspected by a professional technician. They can identify any issues that may require repair or refurbishment.
12. Storage:
· If you plan to store your vehicle for an extended period, consider removing the rims and storing them in a cool, dry place to prevent damage from environmental factors.
By following these maintenance steps, you can keep your rims looking great and functioning properly for years to come. Proper rim maintenance not only enhances the appearance of your vehicle but also contributes to safety and overall vehicle performance.
A motorcycle rim is a vital component of the wheel assembly, serving as the structural foundation for the tire, which in turn, plays a critical role in a motorcycle's overall performance, stability, and safety. The construction of a motorcycle rim is a complex and precisely engineered process, involving a combination of materials, design principles, and manufacturing techniques. In this detailed explanation, we will explore the perplexity and burstiness of this intricate subject.
#MotorcycleRims #RimTypes #Customization #RidingPerformance #MaintenanceTips #BikeUpgrades #TwoWheels #RimSelection #MotorcycleEnthusiast #CruisingInStyle